In News
The Union Cabinet on Wednesday approved a proposal to set up a commission which will examine the issue of sub-categorisation of the Other Backward Classes (OBC).
- It has to examine the “extent of inequitable distribution of benefits of reservation” among various castes and communities that come under the Central OBC list.
- The committee also has to work out the mechanism, criteria and parameters for the actual sub-categorisation. The actual reservation will continue to be 27% and within this the committee will have to do the re-arranging. For example, if the committee comes to the conclusion that in the last many years Yadavs have benefited far more than Khatiks or Sainis then the amount of reservation for them will be increased vis-à-vis the Yadavs.
- The third task is bringing order to the Central list of OBCs by removing any repetitions.
- The National Commission for Backward Classes had recommended it in 2011 and a standing committee too had repeated this.
- Already 11 States, including Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Jharkhand, West Bengal and Jammu region have such a categorisation in State government jobs.
- The Union Cabinet also increased the “creamy layer” ceiling for the Other Backward Classes to RS. 8 lakh per annum from the existing RS. 6 lakh for Central government jobs.
- This means that the umbrella of reservation is widened and those earning up to RS. 8 lakh per annum would now get the benefits.
- In 1992 too the Supreme Court had in a judgment given a similar recommendation.
- The OBC Commission as well as the standing committee have favoured this.
Source : The Hindu
GS II : Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation

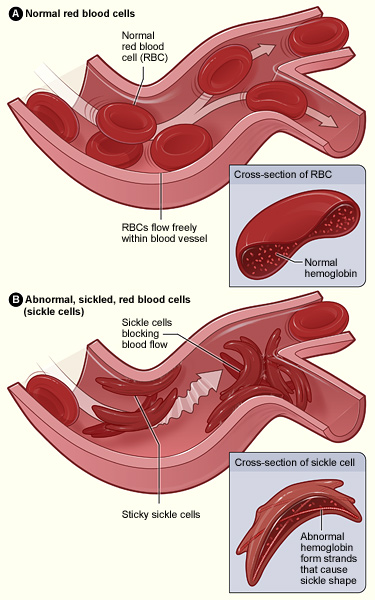 for hemoglobin, a substance composed of a protein (globin) plus an iron molecule (heme) that is
for hemoglobin, a substance composed of a protein (globin) plus an iron molecule (heme) that is 

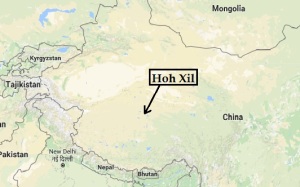 Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, is home to over 200 animal species.
Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, is home to over 200 animal species.