An attempt to minimise paperwork for air travel, the government is looking to roll out a digital system for airport entry and boarding flights using a flier’s Aadhaar number and mobile phone. The proposal came in the name DIGI YATRA
Proposed digi yatra
- The civil aviation ministry is looking to make “boarding pass and security check-in” digital.
- The ministry is working on the initiative to ensure the whole air travel experience is completely digital.
- Under the initiative, there will be no need for any paper and the traveller will be securely identified through Aadhaar number, passport or other documents.
- The government also decided to have a no-fly list in the wake of instances of unruly behaviour by air passengers.
- If passengers behave in an unruly or disruptive manner and endanger the safety in an aeroplane, then he will not able to fly and are appropriately dealt with.
Source : Live Mint
GS II : Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation




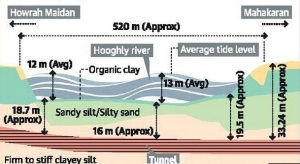
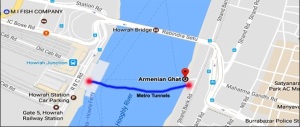 The construction of the first underwater metro tunnel in the country cutting deep inside the bed of the Hooghly river. By the end of July, two tunnels running parallel will connect the twin cities of Howrah and Kolkata located on either side of the Hooghly. The construction is a first in India, the two 520-metre structures are part of a 10.8 km underground stretch and are crucial to the East West Metro project
The construction of the first underwater metro tunnel in the country cutting deep inside the bed of the Hooghly river. By the end of July, two tunnels running parallel will connect the twin cities of Howrah and Kolkata located on either side of the Hooghly. The construction is a first in India, the two 520-metre structures are part of a 10.8 km underground stretch and are crucial to the East West Metro project